In today's globalized and competitive business environment, the supplier
selection process has become a critical activity for organizations across various
industries. The selection of appropriate suppliers directly impacts an organization's ability to maintain a reliable supply chain, control costs, ensure product quality, foster innovation, and achieve overall competitive advantage
[3][4]. A well-defined and executed supplier selection process enables
businesses to minimize risks, maximize value, and build long-term, mutually
beneficial relationships with their supply base. This paper aims to explore the key
criteria for evaluating and selecting suppliers, providing a framework for
organizations to make informed decisions aligned with their strategic objectives.
The Supplier Selection Process
The supplier selection process is a systematic approach that involves several key
stages:
1. Identifying Business Needs: The first step involves clearly defining the
organization's requirements, including the specific products or services
needed, quantity, quality standards, delivery schedules, and any other
relevant specifications.
2. Listing Potential Suppliers: This stage involves identifying potential
suppliers through various sources such as industry networks, online
directories, trade publications, referrals, and market research
3. Determining Selection Criteria: Establishing a comprehensive set of
criteria to evaluate and compare potential suppliers is crucial for making
objective and informed decisions
4. Request for Information/Proposal (RFI/RFP): Qualified suppliers are
then invited to submit RFI/RFPs, providing detailed information about their
capabilities, pricing, quality control processes, and other relevant factors
5. Evaluating and Selecting Suppliers: The evaluation process involves
assessing the submitted proposals against the pre-defined criteria,
conducting site visits or audits if necessary, and shortlisting the most
promising suppliers
6. Negotiating and Finalizing Agreements: The final stage involves
negotiating contract terms, pricing, and service level agreements with the
selected supplier(s)
7. Supplier Relationship Management: Ongoing monitoring of supplier
performance, communication, and collaboration to ensure continuous
improvement and value creation
Key Supplier Selection Criteria
The specific criteria used for supplier selection may vary depending on the
industry, the nature of the product or service being sourced, and the
organization's strategic priorities. However, some core elements should always
be considered :
1. Quality and Safety of Products/Services: This is a fundamental and
non-negotiable requirement. The supplier's ability to consistently meet or
exceed the required quality standards is paramount. Evaluation should
include assessment of certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), quality control
processes, defect rates, and performance history.
2. Cost and Price Structure: While cost should not be the sole determinant,
it remains a significant factor. Organizations should consider the total cost
of ownership, including purchase price, transportation costs, discounts,
payment terms, and potential long-term costs.
3. Delivery and Reliability: Timely and reliable delivery is crucial for
maintaining a smooth supply chain and meeting customer demands.
Factors to consider include the supplier's delivery performance history,
lead times, logistics capabilities, and ability to handle disruptions
4. Financial Stability: Assessing the supplier's financial health is essential
to ensure their long-term viability and ability to meet commitments.
Organizations should review financial statements, credit ratings, and other
relevant indicators to evaluate the supplier's financial stability.
5. Capacity and Scalability: The supplier's capacity to meet current and
future demand is an important consideration , Organizations should
assess the supplier's production capacity, equipment, workforce, and
ability to scale operations as needed.
6. Technology and Innovation: In today's rapidly evolving business
landscape, a supplier's technological capabilities and commitment to
innovation can provide a significant competitive advantage. Assessment
should include their use of advanced technologies, R&D investments, and
ability to develop cutting-edge solutions.
7. Ethical and Environmental Practices: Increasingly, organizations are
considering ethical and environmental factors in their supplier selection
process. This includes assessing the supplier's adherence to fair labor
practices, environmental sustainability initiatives, and commitment to
social responsibility.
8. Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and
collaboration are essential for building strong supplier relationships.
Organizations should evaluate the supplier's communication systems,
responsiveness, and willingness to collaborate on problem-solving and
continuous improvement initiatives.
9. Risk Management and Preparedness: Suppliers should have robust risk
management strategies in place to mitigate potential disruptions to the
supply chain, This includes assessing their ability to handle unforeseen
events such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or geopolitical
instability.
10. Flexibility: The supplier's ability to adapt to changing business needs and
unexpected order changes.
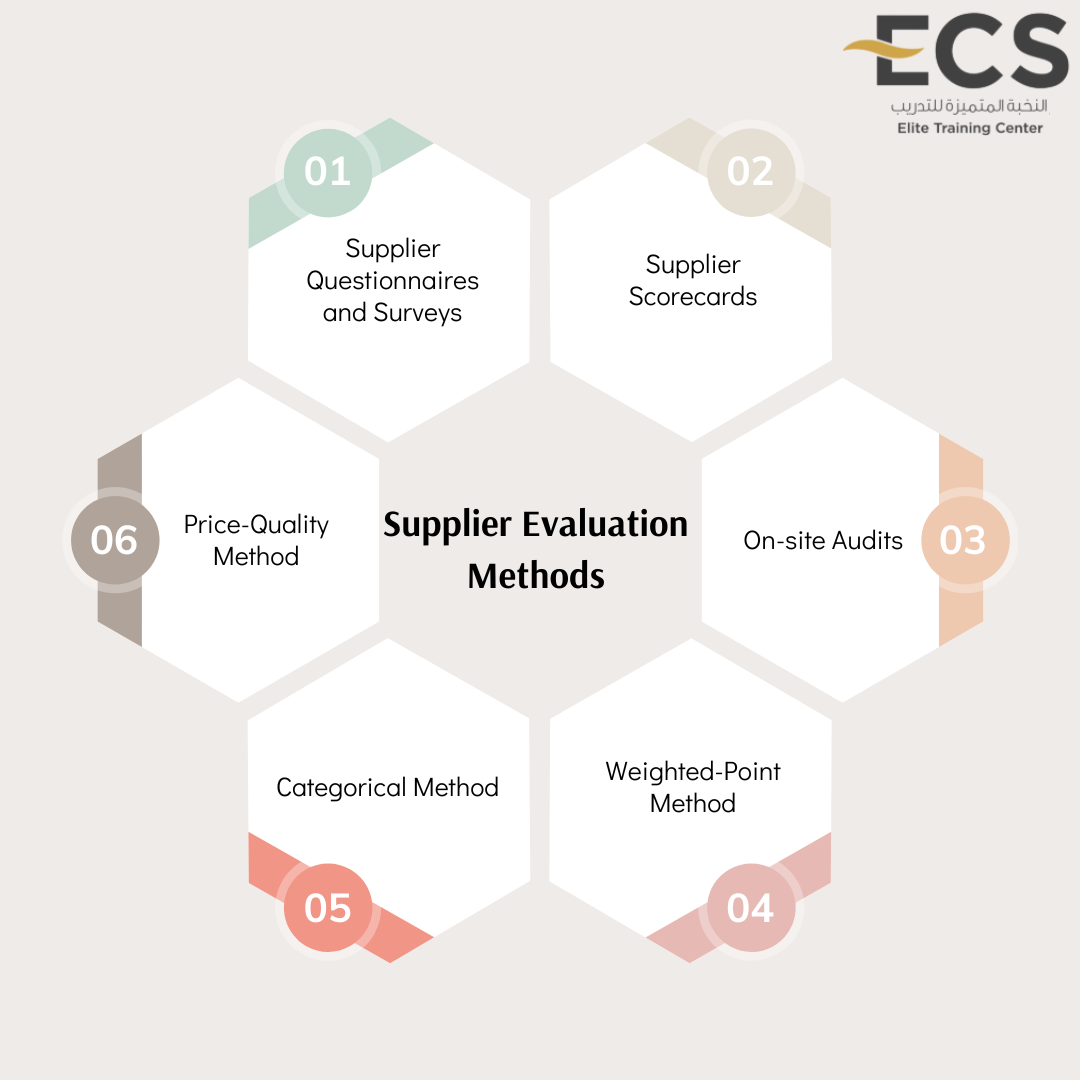
Supplier Evaluation Methods
Various methods can be employed to evaluate suppliers against the defined
criteria:
1. Supplier Questionnaires and Surveys: Standardized questionnaires are
used to gather information from potential suppliers on various evaluation
criteria.
2. Supplier Scorecards: Scorecards provide an objective framework for
evaluating and ranking suppliers based on key performance indicators
(KPIs) such as quality, cost, delivery, and service
3. On-site Audits: Visiting the supplier's premises to conduct audits can
provide valuable insights into their operations, quality control processes,
and adherence to standards.
4. Weighted-Point Method: This quantitative approach involves scoring
suppliers based on criteria weighted according to their importance.
5. Categorical Method: This uncomplicated method uses categorical terms
(e.g., "good," "neutral," "poor") to rate supplier performance against various attributes.
6. Price-Quality Method: This method combines both quantitative and
qualitative evaluation, where companies evaluate both pricing and quality
together to select the supplier that fits both evaluation criteria.
The Importance of Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Supplier selection is not a one-time event but rather the beginning of an ongoing
relationship. Effective Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is crucial for
maximizing the value derived from these relationships. SRM involves developing
trust, fostering open communication, and collaborating with key suppliers to drive
innovation, improve performance, and mitigate risks. By investing in SRM,
organizations can create a competitive advantage through a resilient and high-
performing supply chain.
Challenges in Supplier Selection
Despite the importance of supplier selection, organizations often face several
challenges:
Overemphasis on cost reduction: Focusing solely on price can lead to
neglecting other critical factors such as quality, reliability, and innovation.
Lack of specific SRM competencies: Insufficient skills and knowledge in
managing supplier relationships can hinder effective collaboration and
value creation.
Insufficient alignment: A lack of alignment between business,
procurement, and supplier objectives can lead to conflicts and missed
opportunities.
Information asymmetry: Difficulty in obtaining accurate and reliable
information about potential suppliers can make it challenging to make
informed decisions.
Dynamic market conditions: Rapid changes in market conditions,
technology, and regulations can make it difficult to assess long-term
supplier viability .
Conclusion
Supplier selection is a critical process that significantly impacts an organization's
success, By establishing clear selection criteria, employing appropriate
evaluation methods, and investing in supplier relationship management,
businesses can build strong, resilient, and value-driven supply chains. In addition
to traditional factors like quality, cost, and delivery, organizations must also
consider ethical, environmental, and innovative capabilities when selecting
suppliers [3][23]. Embracing a holistic and strategic approach to supplier
selection enables organizations to mitigate risks, improve performance, and
achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
References
1. Supplier Selection Criteria and Methods in Supply Chains: A Review -
Semantic Scholar
2. Exploring the importance of different supplier selection criteria -
ResearchGate
3. Understanding the Basics of Supplier Selection - NetNada
4. Key Supplier Selection Criteria Every Procurement Executive Should
Know
5. Supplier evaluation and selection: Criteria and methods - Lawcode
6. Supplier Selection Process: A Quick Guide | SafetyCulture
7. How to Perfect Your Supplier Selection Process in 5 Steps - DeepStream
8. Supplier Selection: Choose the Right Supplier | SafetyCulture
9. 5 Steps to Supplier Selection - Transformance Advisors
10. Supplier Evaluation - How to Evaluate Suppliers - CIPS
11. (PDF) Supplier Relationship Management: Strategies for Enhancing
Collaboration and Performance - ResearchGate
12. Supplier Relationship Management and Organizational Performance: A
Focus on Public Procurement - Research leap
13. Criteria for supplier selection: A literature review - ResearchGate
14. Vendor & Supplier Selection Process: Criteria & Best Practices | Infosys
BPM
15. Supplier Selection Criteria — The Ultimate Guide - Procurement Tactics
16. The Complete Guide to Vendor Selection Process - Tipalti
17. What is the Supplier Selection Process | CIPS
18. Five Effective Methods for Selecting Suppliers in the Oil and Gas Industry
19. 6 Methods for Effective Supplier Evaluation - Veridion
20. Supplier Evaluation: The Methods and Benefits - TenderBoard
eProcurement Platform
21. Supplier Relationship Management - CBS Research Portal
22. Supplier Relationship Management How key suppliers drive your
company's competitive advantage - Pwc.nl
23. Assessing the Best Supplier Selection Criteria in Supply Chain
Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic - PMC
Elite Training Center:
www.ellite-t-s.com
Date: 19/10/2025





